
20
Years
180+
Hospitals
700+
Eye Specialists

3
Crore+ Eyes

What is Cornea and its related disorders?
The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped front layer of the eye that helps focus light. It plays a major role in sharp, clear vision — just like a camera lens. Any injury, infection, or disease affecting the cornea can cause irritation, blurred vision, or even vision loss if untreated. Corneal disorders include infections, injuries, degenerations, and inherited conditions that affect corneal clarity or shape. They may cause scarring, swelling, or distortion, making it harder for light to enter the eye properly.
Early diagnosis and treatment prevent long-term damage and protect vision.

Blurred or distorted vision
Redness, irritation or watering

Sensitivity to light (photophobia)

Difficulty wearing contact lenses
Eye pain or foreign body sensation

Visible white/grey spot on the eye

Sudden or gradual vision changes

Keratoconus Cornea becomes thin and cone-shaped, causing distorted, blurry vision.

Corneal Ulcer Infection or injury causes a painful wound, requiring urgent care.

Dry Eye Disease Tear imbalance leads to irritation, burning, and fluctuating vision.

Corneal Dystrophies Inherited conditions causing deposits or clouding inside the cornea.
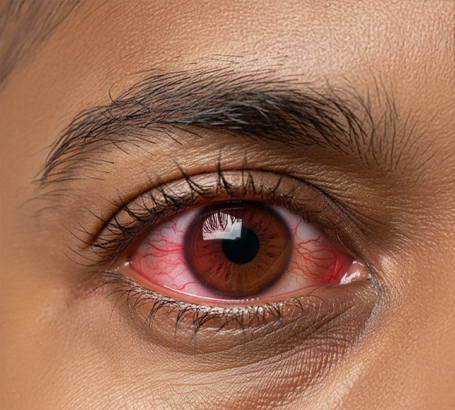
Corneal Scarring / Opacities Injury, infection or surgery leaves a mark affecting clarity and vision.
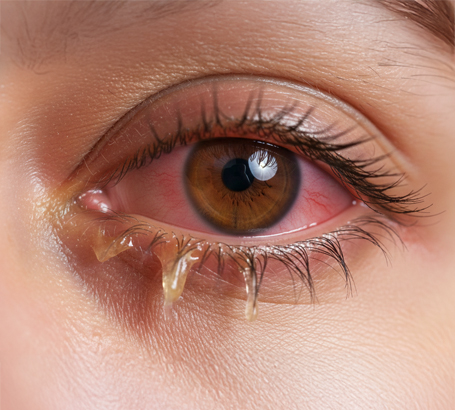
Infections such as bacterial, viral, or fungal eye infections.
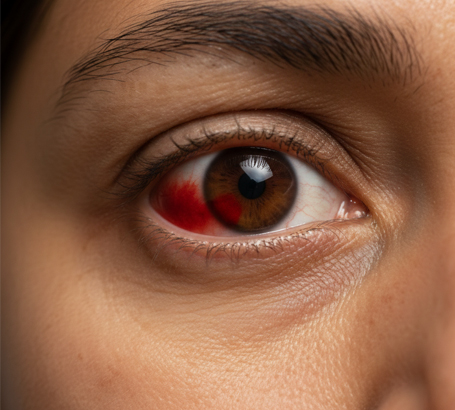
Injuries like scratches, chemicals, or trauma to the eye.

Genetics where some people are born with conditions that affect the cornea.

Dry eyes or inflammation often linked to autoimmune disorders.

Improper contact lens use or wearing lenses for too long.
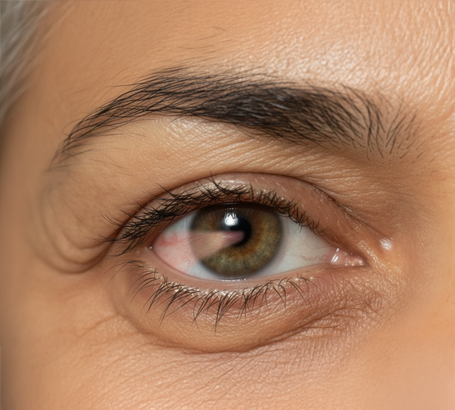
Age-related changes such as conditions that affect the inner corneal cells.
Environmental exposure like too much sunlight or UV rays.

Existing medical conditions such as diabetes, or complications after eye surgery.
Treatment Options for Corneal Disorders
Eye Drops & Medications
Used to treat infections, swelling, inflammation, and dry eye conditions.
Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)
Strengthens a weak cornea in keratoconus to stop further progression.

Specialty Contact Lenses
Custom lenses like scleral or RGP lenses improve clarity in irregular corneas.
Laser Procedures (PTK/PRK)
Smoothens corneal surface irregularities to improve comfort and vision.
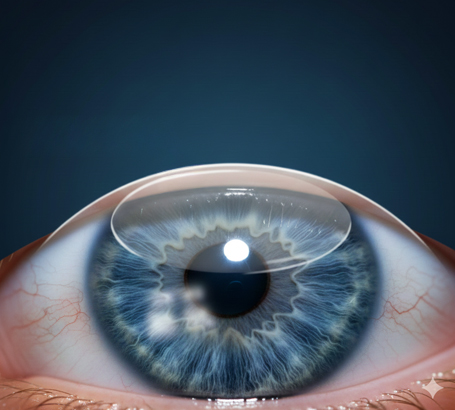
Corneal Transplant (Full or Partial)
Damaged cornea is replaced with healthy donor tissue for vision restoration.
Advanced Technologies for Cornea Care at ASG
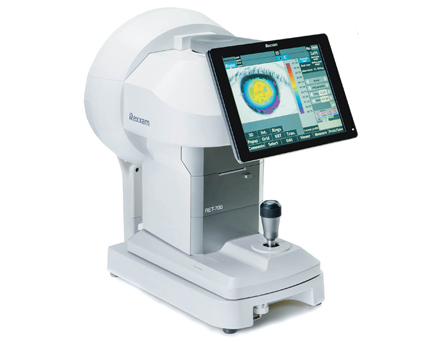
Corneal Topography
Maps corneal shape to detect early keratoconus or other irregularities.
-
Detailed 3D analysis
-
Early disease detection
-
Accurate treatment planning
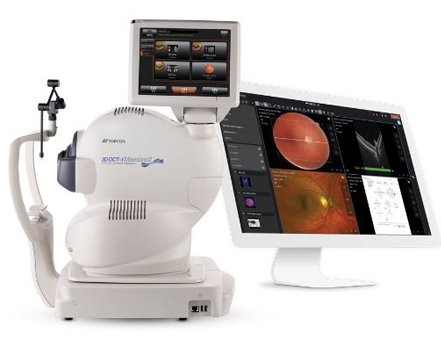
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
High-resolution retinal scan to detect inflammation and early changes.
-
Non-invasive imaging
-
Tracks disease progression
-
Guides treatment decisions

Specular Microscopy
to assess endothelial cell count before and after surgery.
Your Step-by-Step Cornea Care Journey
- Comprehensive corneal evaluation
- Topography/OCT if needed
- Understanding symptoms and lifestyle needs
Consultation
1
- Treatment plan based on corneal condition
- Clear communication on expected outcomes
- Decision on conservative or surgical care
Diagnosis & Planning
2
- Medicines, lenses, laser, or transplant depending on severity
- Minimally invasive options when possible
- Comfort-focused techniques
Treatment
3
- Regular checkups for monitoring
- Long-term care to prevent recurrence or progression
Follow-up & Protection
4
- Comprehensive corneal evaluation
- Topography/OCT if needed
- Understanding symptoms and lifestyle needs
Consultation
1
- Treatment plan based on corneal condition
- Clear communication on expected outcomes
- Decision on conservative or surgical care
Diagnosis & Planning
2
- Medicines, lenses, laser, or transplant depending on severity
- Minimally invasive options when possible
- Comfort-focused techniques
Treatment
3
- Regular checkups for monitoring
- Long-term care to prevent recurrence or progression
Follow-up & Protection
4
Book Your Appointment
Submit Your Request
Get a Call from Our Team
Meet Your Specialist
Begin Your Eye Care Journey
Please wait...
Self Booking
Get A Call Back
Vision for All.
Not Just for Some
ASG is growing its network with 200 Vision Centres, delivering affordable eye care to over 4 million people.
Or
Clear Answers for Better Vision
What is the cornea?
The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped outermost layer at the front of the eye. Often referred to as the “window of the eye,” it plays a vital role in focusing light and protecting the inner structures of the eye from dust and germs.
What are the most common corneal problems?
Our specialists at ASG frequently treat a variety of corneal conditions, including:
Keratitis: Inflammation or infection often caused by bacteria or viruses.
Corneal Abrasions: Scratches on the surface of the eye.
Corneal Ulcers: Serious open sores usually resulting from infection.
Keratoconus: A condition where the cornea thins and bulges into a cone shape.
Corneal Dystrophies (e.g., Fuchs’ Dystrophy): Genetic conditions causing cloudiness.
Pterygium: A non-cancerous growth that can spread onto the cornea.
What symptoms might indicate a corneal problem?
You should visit a specialist if you experience:
Blurred or distorted vision.
Persistent eye pain or redness.
Extreme light sensitivity (photophobia).
Excessive tearing or unusual discharge.
The sensation of having a foreign object in your eye.
How is a corneal condition diagnosed at ASG Eye Hospital?
We use advanced diagnostic technology, including Slit-Lamp Microscopy and Corneal Topography, to map the surface of your eye. These tools allow our surgeons to observe individual corneal layers and detect microscopic changes early.
Can a scratched cornea heal on its own?
While minor abrasions may heal within 24–48 hours, they should always be evaluated by a professional. An untreated scratch can lead to a Corneal Ulcer or serious infection, which can permanently impair your vision.
What treatment options are available for corneal diseases?
At ASG, treatment is customized based on the diagnosis:
Medical Management: Specialized antibiotic or anti-inflammatory eye drops.
Specialty Contact Lenses: Scleral or Rose-K lenses for Keratoconus.
C3R (Corneal Collagen Cross-linking): To strengthen the cornea and stop the progression of Keratoconus.
Corneal Transplant: Replacing damaged tissue with healthy donor tissue.
What is a corneal transplant (Keratoplasty)?
A corneal transplant is a surgical procedure where a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced with healthy donor tissue. ASG Eye Hospital is equipped with advanced surgical suites to perform both full-thickness and partial-thickness (DALK/DSEK) transplants.
How safe is a corneal transplant?
Corneal transplants are highly successful. While all surgeries carry some risk, such as graft rejection or infection, our surgeons use precision techniques to minimize these. Regular post-operative follow-ups at ASG ensure the best long-term results.
How can I prevent corneal injuries and diseases?
Always wear protective eyewear during sports or industrial work.
Maintain strict hygiene if you wear contact lenses (never sleep in them).
Treat chronic “Dry Eye” promptly to prevent surface damage.
Schedule regular eye exams to catch genetic conditions early.
When should I see an ASG Cornea Specialist?
Seek immediate care if you experience sudden vision loss, persistent pain after an injury, or if you have a “white spot” appearing on the clear part of your eye. Early intervention is the key to preventing permanent scarring.
Every Angle of Vision.
Every Kind of Care.

Cataract
What do you understand by Cataract? A cataract is an eye condition characterized by the clouding of the natural lens in the eye, leading to vision

Diabetic Retinopathy
What Do You Understand by Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition, it is caused by diabetes
Cornea
Cornea and Associated Diseases The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior parts of an eye.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma: A Silent Thief of Sight Glaucoma is an eye condition that directly damages the optic nerve (the bundle of nerve fibers that carries..
Neuro-Ophthalmology
What is Neuro-Ophthalmology? Neuro ophthalmology is a combination of super specialty of both neurology and ..
