
Gentle Care, Clear Futures, Specialized Eye Care for Your Child

20
Years
180+
Hospitals
700+
Eye Specialists

3
Crore+ Eyes

What is Pediatric Ophthalmology?
Pediatric ophthalmology focuses on detecting and treating eye problems in children from infancy to teenage years. Children’s eyes are still developing, which makes early detection essential for lifelong healthy vision. Timely care helps prevent issues that can affect learning, development, and overall quality of life.
What are the Common Pediatric Eye Conditions?
Children can experience a range of issues including refractive errors, lazy eye, squint, congenital problems, and more. Most of these conditions can be treated effectively when identified early. Regular eye check-ups ensure problems don’t go unnoticed or untreated.


Frequent eye rubbing or blinking

Holding devices or books very close

Squinting, closing or covering one eye

Complaints of headaches or eye pain
White or grey reflex in photographs

Poor attention span or difficulty reading

Wandering or misaligned eyes (squint)
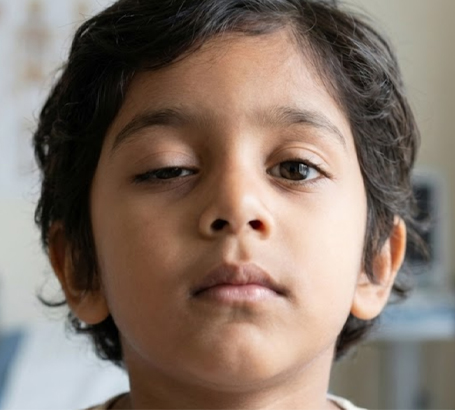

Pediatric Ptosis : Drooping eyelid that can block vision and hinder development.
.
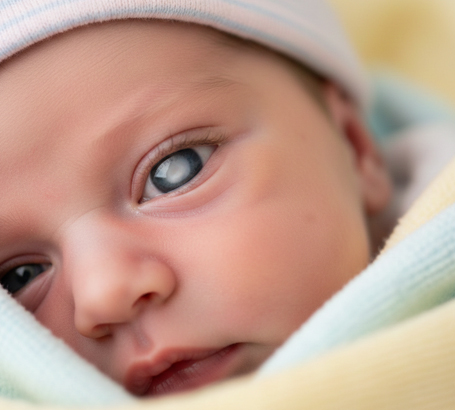

Congenital Cataract : Lens clouding present from birth, affecting early visual development.
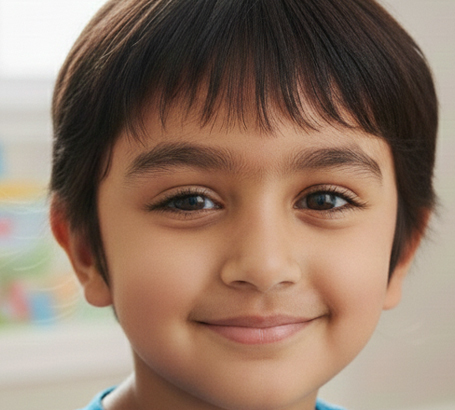

Strabismus (Squint) : Eyes are misaligned, affecting binocular vision and depth perception.
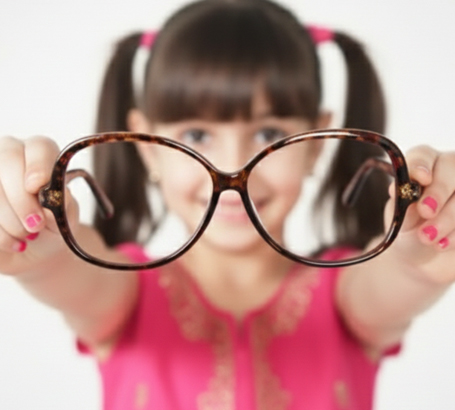

Refractive Errors (Myopia, Hyperopia, Astigmatism): Difficulty seeing clearly due to needing spectacles for distance or near.
Amblyopia (Lazy Eye) : One eye has weaker vision because the brain favours the other.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Ophthalmology

Spectacles & Vision Therapy
Improve clarity, strengthen weaker eyes, and support proper visual development.

Patching for Lazy Eye
Covers the stronger eye to train and strengthen the weaker one.

Squint Correction (Surgery or Glasses)
Aligns the eyes to restore coordinated, binocular vision.
Pediatric Cataract Surgery
Removes cataracts in infants/children for proper vision development.

Myopia Management Treatments
Special lenses, eye drops, or lifestyle guidance to slow power progression.
Why us ?
We understand that children may feel anxious before check-ups, so our empathetic doctors take time to comfort, reassure, and make every visit calm, safe, as well as stress-free. ASG offers child-focused eye care with gentle exams, kid-friendly technology, and specialists trained to handle everything from simple vision issues to complex conditions
Advanced technologies for Pediatric Ophthalmic Management at ASG

Digital Vision Screening
-
Child-safe machines
-
Quick and accurate check ups
-
Zero discomfort
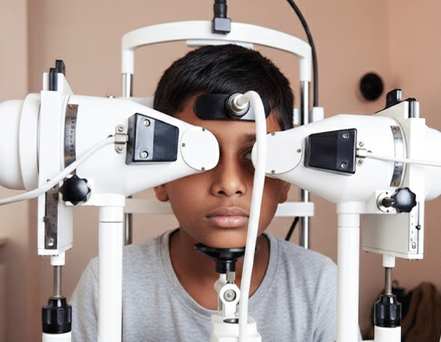
Squint & Eye Alignment Testing Systems:
-
Advanced tools for accurate eye alignment
-
Accurate and early diagnosis of squint
-
Personalised vision correction therapy
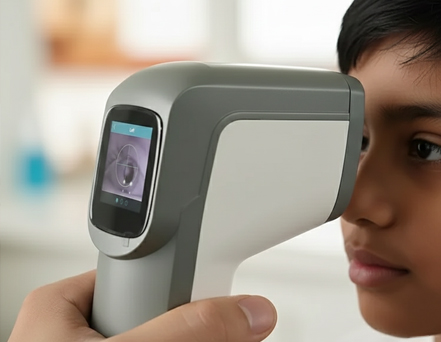
Handheld Retinoscopy & Autorefractors:
-
Advanced devices to measure glasses power for babies and toddlers
-
Alternative options for babies who cannot read charts

Pediatric OCT (if needed)
-
No-touch, high-resolution scan
-
Helps detect retina or optic nerve issues early
-
Completely safe and comfortable for children

Amblyopia (Lazy Eye) Monitoring Tools
-
Tracks improvement during patching or therapy
-
Helps ensure the best vision outcomes
-
Makes progress easy for parents to understand
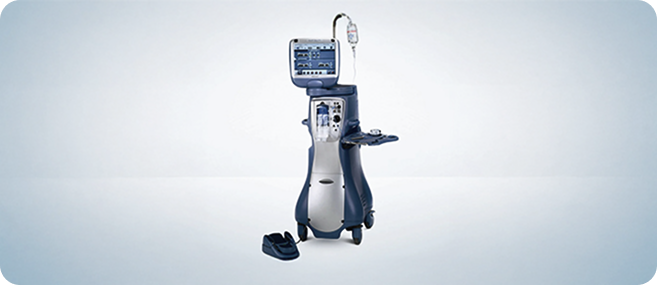
Specialized Pediatric Surgical Equipment
-
Miniature, child-specific instruments
-
Ensures safe, precise surgeries when required
-
Designed for delicate pediatric eye structures
The Pediatric Ophthalmology Surgery Journey
A friendly, child-focused eye check-up to assess vision, eye alignment, and overall eye health. Doctors explain everything in simple terms to parents.
Consultation & Planning
1
If any issue is found—like myopia, squint, lazy eye, or allergies—you get a clear explanation, treatment options, and practical advice for daily care.
Diagnosis & Guidance
2
From glasses to patching therapy to advanced pediatric procedures, every treatment is designed to be gentle, safe, and child-friendly.
Treatment
3
Regular check-ups ensure your child’s eyes grow healthy and strong, with timely adjustments to treatment as they develop.
Follow-ups & Monitoring
4
A friendly, child-focused eye check-up to assess vision, eye alignment, and overall eye health. Doctors explain everything in simple terms to parents.
Consultation & Planning
1
If any issue is found—like myopia, squint, lazy eye, or allergies—you get a clear explanation, treatment options, and practical advice for daily care.
Diagnosis & Guidance
2
From glasses to patching therapy to advanced pediatric procedures, every treatment is designed to be gentle, safe, and child-friendly.
Treatment
3
Regular check-ups ensure your child’s eyes grow healthy and strong, with timely adjustments to treatment as they develop.
Follow-ups & Monitoring
4
Book Your Appointment
Submit Your Request
Get a Call from Our Team
Meet Your Specialist
Begin Your Eye Care Journey
Please wait...
Self Booking
Get A Call Back
Vision for All.
Not Just for Some
ASG is growing its network with 200 Vision Centres, delivering affordable eye care to over 4 million people.
Or
Clear Answers for Better Vision
What is Pediatric Ophthalmology?
Pediatric Ophthalmology is a sub-specialty of eye care that deals with the vision development and eye health of infants, children, and adolescents. Because a child’s visual system is still developing until age 8–10, early intervention by a specialist is crucial to prevent permanent vision loss.
At what age should a child have their first eye exam?
A child should have their first comprehensive eye screening at 6 months of age, followed by another at age 3, and then annually once they start school. However, if you notice your child squinting, rubbing their eyes, or holding books very close, you should schedule an appointment immediately.
What is a "Squint" (Strabismus)?
A squint is a condition where the eyes do not look in the same direction at the same time. One eye may turn in, out, up, or down while the other eye looks straight ahead. At ASG, we treat squints using specialized exercises, glasses, or advanced muscle-realignment surgery.
Can a squint be corrected at any age?
Yes. While it is best to treat a squint in early childhood to ensure proper vision development, squint surgery can be performed on adults as well to improve eye alignment and facial appearance.
What is Amblyopia or "Lazy Eye"?
Amblyopia occurs when the brain favors one eye over the other, leading to poor vision in the “lazy” eye. If not treated during the “critical period” of childhood (usually before age 7 or 8), the vision loss in that eye may become permanent.
How is a Lazy Eye treated at ASG Eye Hospital?
Treatment often involves “Patching Therapy,” where the stronger eye is covered with a patch for a few hours a day to force the brain to use the weaker eye. We also offer Vision Therapy and specialized glasses to help strengthen the visual connection.
How do I know if my child has vision problems?
Watch for these warning signs:
Sitting too close to the TV.
Tilting the head to see better.
Frequent eye rubbing or watering.
Closing one eye to read or look at distant objects.
Complaints of headaches or “tired eyes” after school.
Does ASG provide surgery for congenital cataracts?
Yes. Some babies are born with cataracts (cloudy lenses). This is a medical priority, as it prevents light from reaching the retina during critical development. Our pediatric surgeons are experts in infant cataract surgery and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation.
Are the diagnostic tests painful for children?
Not at all. Our pediatric wings are designed to be child-friendly. We use “no-touch” diagnostic tools and specialized dilating drops to examine the retina. Our doctors are trained to perform exams through play and engagement to keep the child relaxed.
Will my child have to wear glasses forever?
Not necessarily. Many children’s eye shapes change as they grow, and their prescription may decrease. For those with high refractive errors, we monitor them closely and discuss permanent correction options once they reach adulthood.
Every Angle of Vision.
Every Kind of Care.

Cataract
What do you understand by Cataract? A cataract is an eye condition characterized by the clouding of the natural lens in the eye, leading to vision

Diabetic Retinopathy
What Do You Understand by Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition, it is caused by diabetes
Cornea
Cornea and Associated Diseases The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior parts of an eye.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma: A Silent Thief of Sight Glaucoma is an eye condition that directly damages the optic nerve (the bundle of nerve fibers that carries..
Neuro-Ophthalmology
What is Neuro-Ophthalmology? Neuro ophthalmology is a combination of super specialty of both neurology and ..