
20
Years
180+
Hospitals
700+
Eye Specialists

3
Crore+ Eyes

What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
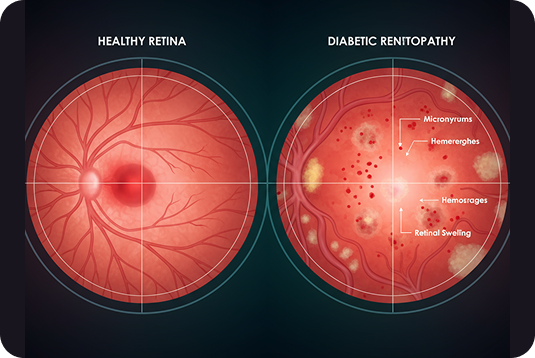
Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye condition where high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in the retina this starts affecting the retina’s ability to form clear images. If not treated early, it can lead to blurred vision, severe vision loss, or in cases of neglect, blindness.
What is the Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy?
There are several treatment routes for this. Treatment depends on the stage at which Diabetic retinopathy is detected and may include laser therapy, injections, or advanced retinal procedures to stop leakage and protect vision. But early diagnosis can help prevent major damage in the long run. It is a silent thief of sight, hence, regular eye check-ups are essential, even when vision feels normal.

Blurred or fluctuating vision

Small dark spots or lines in the vision

Difficulty reading or seeing at night

Colours appearing washed out

Sudden vision loss in advanced stages
Eye pressure or discomfort (sometimes)
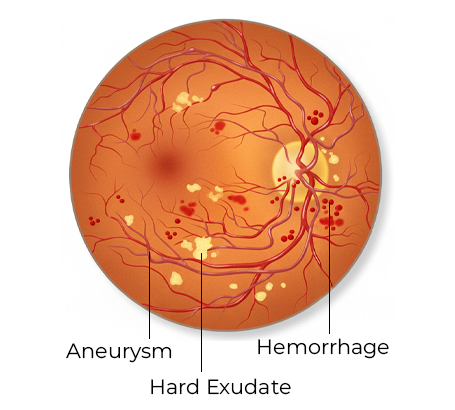
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) Early stage where weakened blood vessels leak or swell, affecting vision slowly.
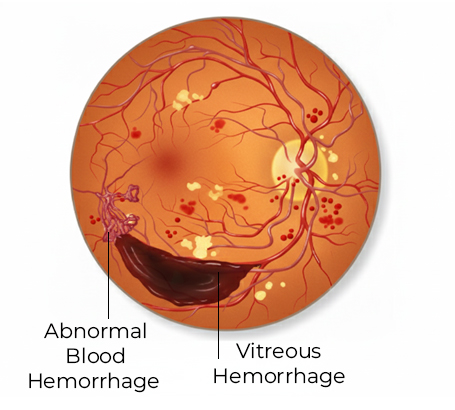
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Advanced stage where new fragile vessels grow, causing bleeding and rapid vision loss.
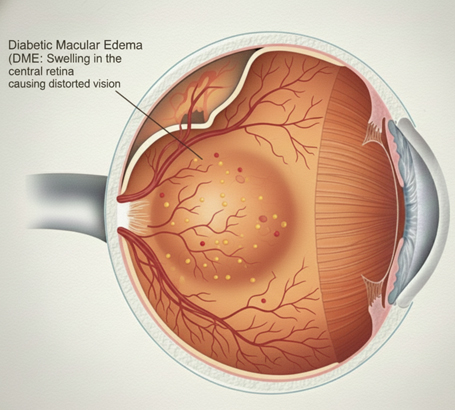
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Swelling in the central retina (macula) leading to blurred, distorted vision.
Vitreous hemorrhage Bleeding inside the eye causing sudden vision loss
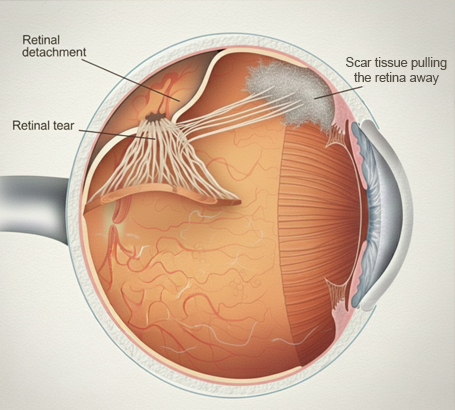
Retinal Detachment Scar tissue pulls the retina away, leading to vision loss

Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Swelling in the central retina (macula) leading to blurred, distorted vision.

Neovascular glaucoma New abnormal vessels block fluid drainage, raising pressure and damaging the optic nerve.

Permanent blindness Heavily advanced, untreated retinopathy can result in irreversible vision loss over several years.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
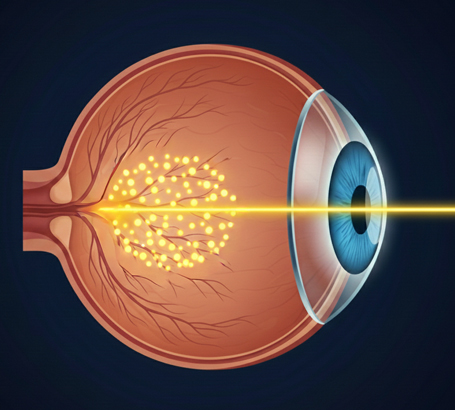
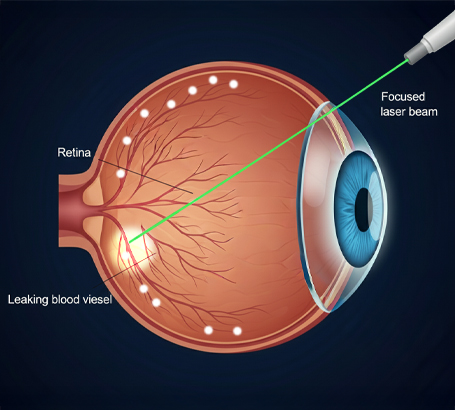
Laser Photocoagulation:
A focused laser seals leaking vessels and prevents further vision loss.
Stong blood sugar & BP control
Excellent diabetes management slows progression and protects long-term vision.
Intravitreal Injections
Painless, anti-VEGF or steroid injections reduce swelling and stop abnormal vessel growth.
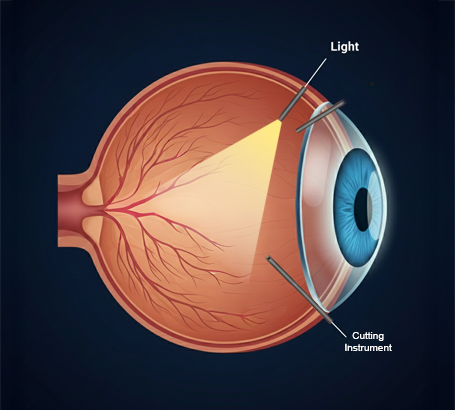
Vitrectomy surgery
A surgical procedure to remove blood, scar tissue, or traction from inside the eye.
Why us ?
ASG offers early, accurate detection of diabetic eye damage and gentle, effective treatments that help protect your vision. With expert retina doctors and advanced tools, we prevent vision loss and keep your eyes healthy for the long run.
Advanced technologies for Diabetic Retinopathy management at ASG
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
High-resolution retinal scan to detect inflammation and early changes.
-
Non-invasive imaging
-
Tracks disease progression
-
Guides treatment decisions
FFA
A dye-based test that shows leakage and blockages in retinal vessels.
-
Maps damaged areas precisely
-
Helps plan laser treatment
-
Essential in advanced cases
Retinal Laser System
Safe, targeted laser that seals leaks and prevents further damage.
-
Quick outpatient procedure
-
Protects remaining vision
-
Stops disease progression
Your Step-by-Step Diabetic Retinopathy Care Journey
- Comprehensive retina exam
- OCT / angiography if needed
- Discussion of severity and treatment plan
Consultation
1
- Choice of treatment
- Guidance on diabetes control
- Clear expectations and timelines
Treatment Planning
2
- Quick outpatient procedures
- Advanced retina technology
- Minimal discomfort, maximum precision
Treatment
3
- Regular monitoring of retinal health
- Adjusting treatment based on changes
- Long-term protection against vision loss
Follow-up & Maintenance
4
- Choice of treatment
- Guidance on diabetes control
- Clear expectations and timelines
Consultation
2
- Detailed pre-surgery checks
- Guidance on medications as needed.
- Step by step surgery walkthrough.
Treatment Planning
2
- Quick outpatient procedures
- Advanced retina technology
- Minimal discomfort, maximum precision
Treatment
3
- Regular monitoring of retinal health
- Adjusting treatment based on changes
- Long-term protection against vision loss
Follow-up & Maintenance
4
Book Your Appointment
Submit Your Request
Get a Call from Our Team
Meet Your Specialist
Begin Your Eye Care Journey
Please wait...
Self Booking
Get A Call Back
Vision for All.
Not Just for Some
ASG is growing its network with 200 Vision Centres, delivering affordable eye care to over 4 million people.
Or
Clear Answers for Better Vision
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It is caused by damage to the tiny blood vessels in the retina—the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. If left untreated, it can lead to severe vision loss or permanent blindness.
What causes this condition?
Consistently high blood sugar levels damage the retinal blood vessels over time. These vessels may swell and leak fluid or close off completely, blocking blood flow. In advanced stages, the eye grows abnormal new blood vessels (proliferative retinopathy) that are fragile and prone to bleeding.
Who is at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy?
Anyone with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes is at risk. The longer you have lived with diabetes, the higher the risk becomes. Other contributing factors include poorly controlled blood sugar, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and pregnancy.
What are the common symptoms?
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy often has no symptoms. As the condition progresses, you may notice:
Floating spots or dark strings (floaters).
Blurred or fluctuating vision.
Dark or empty areas in your field of vision.
Difficulty perceiving colors.
Sudden vision loss in severe cases.
How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed at ASG Eye Hospital
Our specialists use a comprehensive dilated eye exam to view the retina clearly. We also utilize advanced diagnostic technology, including:
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography): To get high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina.
How often should diabetic patients get an eye check-up?
Early detection is vital. We recommend a dilated eye exam at least once a year, even if your vision feels perfectly normal. If retinopathy is already present, our doctors may suggest more frequent visits to monitor progression.
Is it possible to prevent diabetic retinopathy?
While you cannot always prevent it, you can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss. Proper management of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol, combined with regular eye screenings at an ASG branch, is the best way to protect your sight.
What advanced treatments are available at ASG?
Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease and may include:
Intravitreal Injections: Advanced medications to reduce retinal swelling.
Laser Photocoagulation: To seal leaking blood vessels and shrink abnormal ones.
Vitrectomy: A specialized surgery for advanced cases involving significant bleeding or retinal scarring.
Are the treatments painful?
No. Most treatments are performed under local anesthesia or using numbing eye drops. While you may feel a slight sensation of pressure during an injection or laser session, the procedures are generally quick and comfortable.
Can my vision be restored after treatment?
Treatment is highly effective at stopping or slowing further vision loss. In many cases, early intervention can also improve existing vision. However, because retinal tissue is delicate, the goal is to treat the condition before permanent damage occurs.
Every Angle of Vision.
Every Kind of Care.

Cataract
What do you understand by Cataract? A cataract is an eye condition characterized by the clouding of the natural lens in the eye, leading to vision

Diabetic Retinopathy
What Do You Understand by Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition, it is caused by diabetes
Cornea
Cornea and Associated Diseases The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior parts of an eye.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma: A Silent Thief of Sight Glaucoma is an eye condition that directly damages the optic nerve (the bundle of nerve fibers that carries..
Neuro-Ophthalmology
What is Neuro-Ophthalmology? Neuro ophthalmology is a combination of super specialty of both neurology and ..
