
Advanced Care for Your Retina, Protecting Your Most Vital Vision

20
Years
180+
Hospitals
700+
Eye Specialists

3.0
Crore+ Eyes

What are Retinal Disorders?
Retinal disorders are conditions that affect the retina — the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that turns light into the images we see. When the retina is damaged by disease, bleeding, swelling, or a tear, it can cause blurred vision, dark spots, or sudden vision loss. Early detection and timely treatment are crucial to protect vision and prevent permanent damage.
Treatments aim to stop damage, reduce swelling or bleeding, and repair any structural problems in the retina. Depending on the condition, treatments range from injections and laser therapy to minimally invasive surgery.
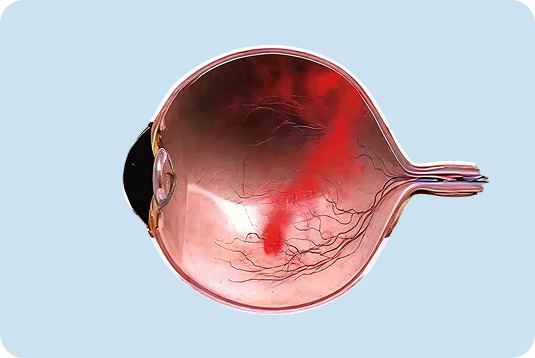
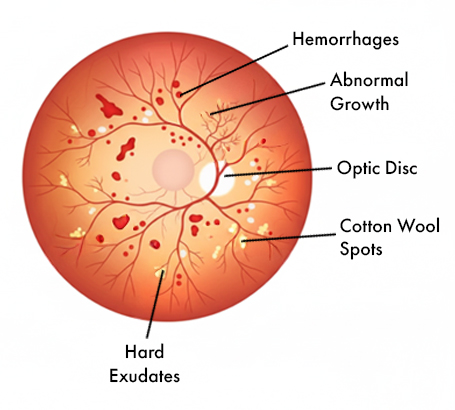
Diabetic Retinopathy Damage and leaking of retinal blood vessels due to diabetes.
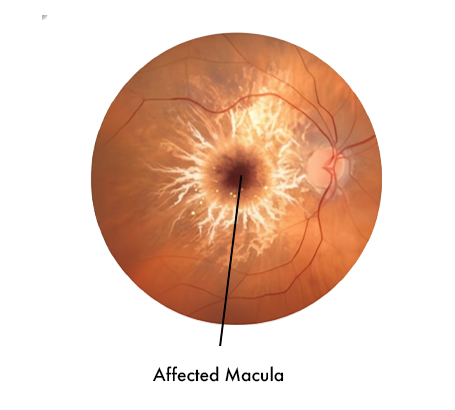
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Degeneration of the central retina (macula) causing loss of central vision.
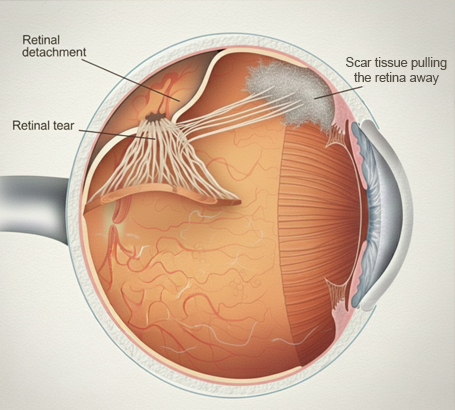
Retinal Detachment Scar tissue pulls the retina away, leading to vision loss
Macular Edema Swelling of the central retina that blurs and distorts vision.
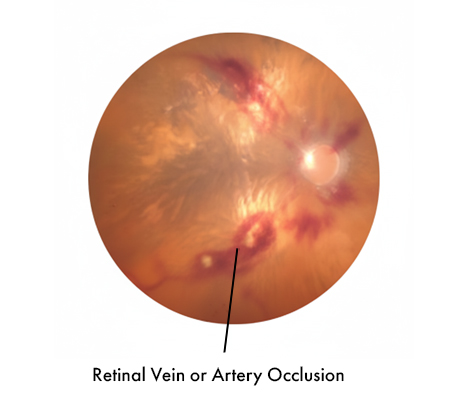
Retinal Vein or Artery Occlusion Blockage of retinal blood flow causing sudden vision changes.
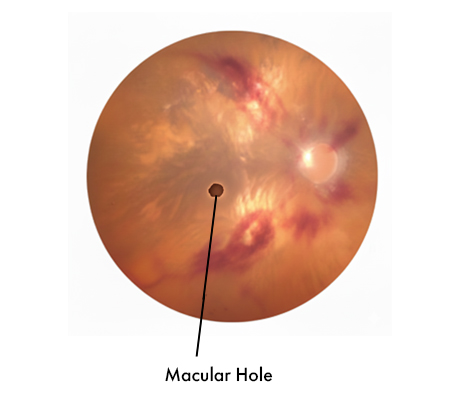
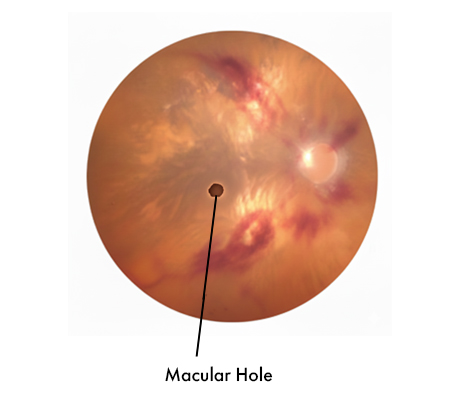
Macular Hole A small break in the central retina causing distorted or missing central vision.
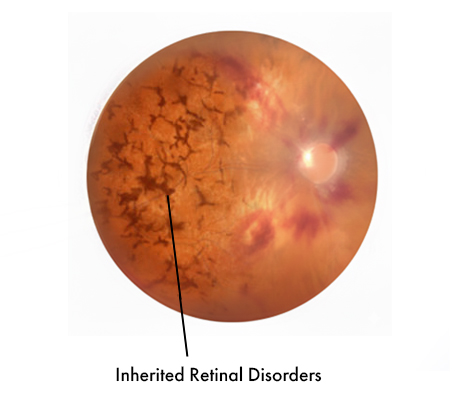
Inherited Retinal Disorders Genetic conditions that progressively affect retinal cells (e.g., retinitis pigmentosa).

Sudden or gradual blurring of vision
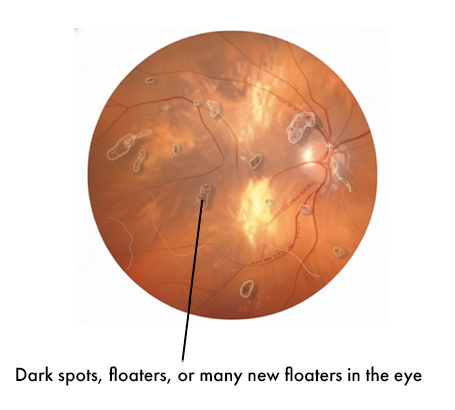
Dark spots, floaters, or many new floaters in the eye

Flashes of light in peripheral vision

Distorted or wavy central vision (metamorphopsia)

A shadow or curtain over part of the visual field (possible detachment)
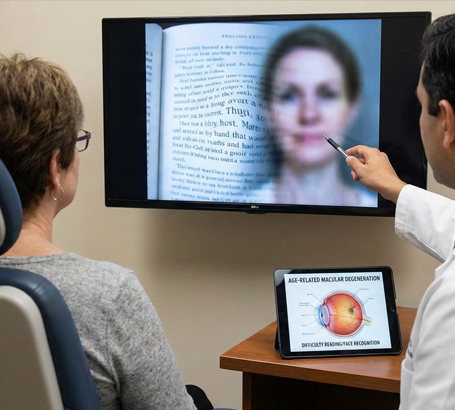
Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
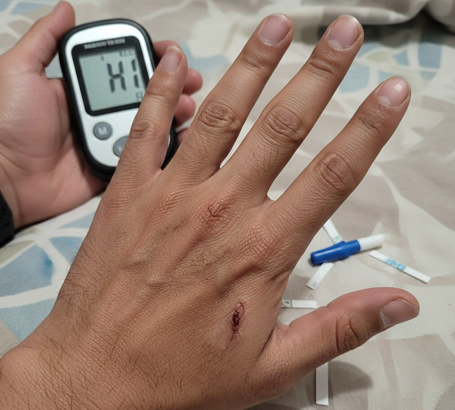
Long-standing diabetes or poorly controlled blood sugar
Age-related degeneration of retinal tissue

High myopia (very short-sighted eyes)
Eye injury or blunt trauma
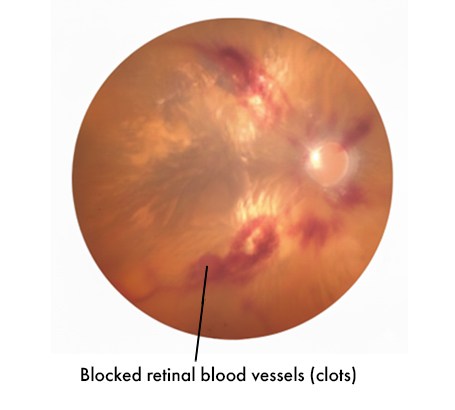
Blocked retinal blood vessels (clots)
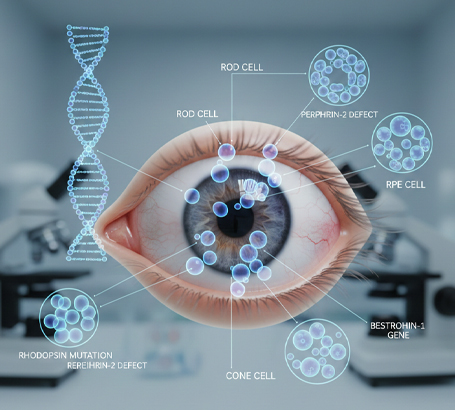
Genetic mutations affecting retinal cells
Inflammation or infection inside the eye
Treatments for Retina Diseases
Treatment depends on the specific retina problem and how advanced it is. Common options include:
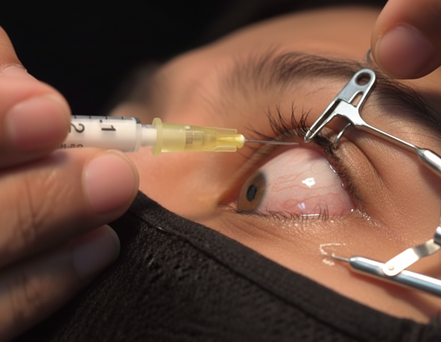
Intravitreal Injections
Anti-VEGF or steroid drugs injected into the eye to reduce abnormal vessel growth and fluid leakage (used for AMD, diabetic macular edema).
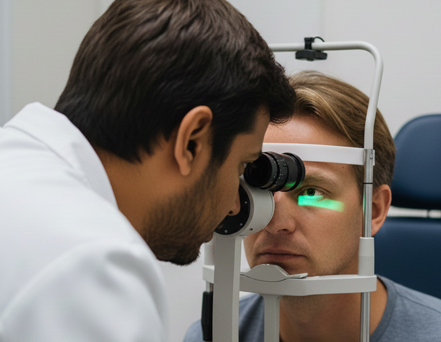
Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation)
Focused laser spots to seal leaking vessels or treat areas at risk (commonly used in diabetic retinopathy).
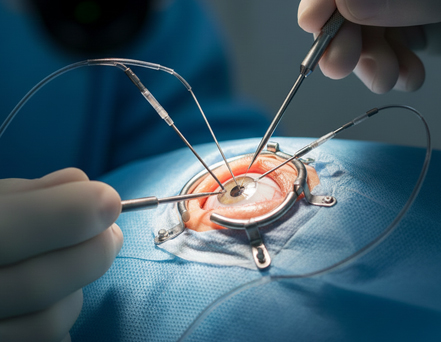
Vitrectomy
Microsurgery to remove the vitreous gel, repair retinal tears or detachments, and clear persistent blood in the eye.
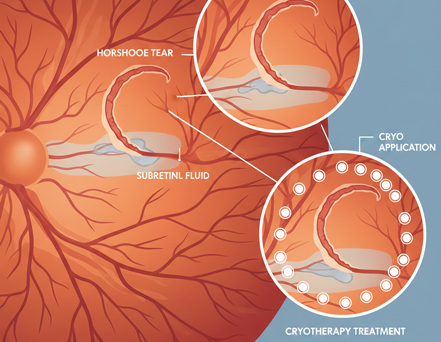
Retinal Cryopexy
Freezing treatment to seal retinal tears and create scar tissue that prevents detachment.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
A light-activated drug plus laser to target abnormal vessels in certain forms of AMD.
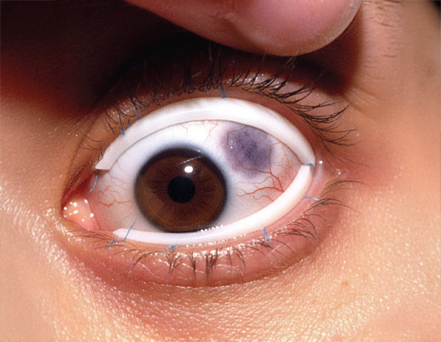
Scleral Buckling
A band placed around the eye to support and reattach the retina in some detachments.
Intravitreal Implants
Long-acting implants that steadily release medication inside the eye for chronic swelling.

Oral/Systemic Medications
Steroids or other drugs for inflammation or specific retinal conditions when appropriate.

Gene Therapy & Emerging Treatments
Cutting-edge options under specialist care for certain inherited retinal diseases.
Why Choose ASG for Retina Care?
ASG combines experienced retinal specialists with advanced diagnostic imaging (OCT, FFA), precision laser systems, and surgical theatres equipped for modern vitreoretinal procedures. We deliver personalised treatment plans, quick in-clinic injections and laser therapy, and safe, minimally invasive surgeries when needed — all with attentive follow-up to preserve and restore your vision.
Your Step-by-Step Retina Care Journey
Comprehensive eye exam, medical history review, vision and visual field tests.
Consultation & Screening
1
OCT (retinal scan), fundus photography, and other tests to pinpoint the problem.
Advanced Imaging & Tests
2
Clear explanation of the condition, risks, and best treatment options personalised for you.
Diagnosis & Treatment Plan
3
In-office injections or laser, or day-care/minimally invasive surgery (vitrectomy, buckling) as required.
Treatment
4
Follow-up imaging and visits to track response, additional treatments if needed, and vision rehabilitation when necessary.
Recovery & Rehabilitation
5
Regular checks to detect recurrence or progression and to protect long-term vision.
Long-Term Monitoring
6
Book Your Appointment
Submit Your Request
Get a Call from Our Team
Meet Your Specialist
Begin Your Eye Care Journey
Please wait...
Self Booking
Get A Call Back
Vision for All.
Not Just for Some
ASG is growing its network with 200 Vision Centres, delivering affordable eye care to over 4 million people.
Or
Clear Answers for Better Vision
What are retinal diseases and how do they affect vision?
Retinal diseases are conditions that affect the retina — the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that helps you see. Damage to the retina can cause blurred vision, floaters, dark spots, or sudden vision loss if not treated early.
What are the most common types of retinal disorders?
Common retinal disorders include diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), retinal detachment, macular edema, retinal vein/artery occlusion, and inherited retinal diseases like retinitis pigmentosa.
What symptoms suggest a retinal problem?
Symptoms may include sudden or gradual blurred vision, floaters, flashes of light, distorted or wavy vision, shadows in vision, or difficulty reading/recognizing faces.
What causes retinal diseases?
Causes include poorly controlled diabetes, aging, high myopia (severe nearsightedness), eye injury, blocked retinal blood vessels, genetic conditions, and inflammation or infection inside the eye.
How are retinal diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive eye exam with tests such as OCT (retinal scan), fundus photography to pinpoint exactly what part of the retina is affected.
Can retinal diseases be treated without surgery?
Yes depending on the condition, treatments include intravitreal injections to reduce swelling, laser therapy to seal leaking vessels, and medications. Not all cases require surgery.
When is surgery needed for retina problems?
Surgery (like vitrectomy or scleral buckling) may be necessary for advanced cases such as retinal detachment or when other treatments don’t improve vision.
What is diabetic retinopathy and how is it treated?
Diabetic retinopathy is a retina disease caused by diabetes damaging tiny blood vessels. Treatment may include strict blood sugar control, laser therapy, injections, or surgery in advanced stages.
Is age-related macular degeneration (AMD) curable?
AMD cannot be completely cured, but early diagnosis and treatment can slow progression and preserve central vision. Options may include injections, laser procedures, or lifestyle changes.
How often should I get my retina checked if I have risk factors?
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, high myopia, or a family history of retinal diseases, regular retina exams (often yearly or more frequent) are recommended to catch changes early.
How can I book a consultation with a retina specialist at ASG Eye Hospital?
You can book online through the ASG Eye Hospital website, call the toll-free number, or visit any ASG location — and the team will help you schedule a retina specialist appointment.
Every Angle of Vision.
Every Kind of Care.

Cataract
What do you understand by Cataract? A cataract is an eye condition characterized by the clouding of the natural lens in the eye, leading to vision

Diabetic Retinopathy
What Do You Understand by Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition, it is caused by diabetes
Cornea
Cornea and Associated Diseases The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior parts of an eye.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma: A Silent Thief of Sight Glaucoma is an eye condition that directly damages the optic nerve (the bundle of nerve fibers that carries..
Neuro-Ophthalmology
What is Neuro-Ophthalmology? Neuro ophthalmology is a combination of super specialty of both neurology and ..